Virtualization
The use of virtualization in network and compute components is not something new. These protocols provide example of virtualization technologies that have been existing for decades. ![]()
NIC teaming / trunking / bundling / bonding / channeling
Create a single logical bonded interface out of 2 or more NIC slaves. Especially used in the context of LAG.
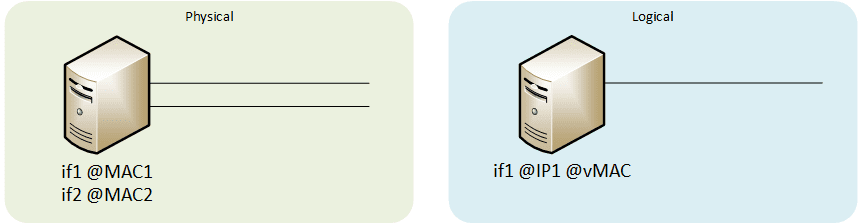
Link Aggregation Group (LAG)
Aggregation of multiple network connections in order to provide higher throughput and provide redundancy.
- Round robin: transmit alternate packets in sequential order from first slave to last slave
- Active-backup: a different backup slave becomes active only if the active slave fails
- XOR: selection of the slave based on MAC address / IP address / Port number
- Broadcast: transmit on all the slaves
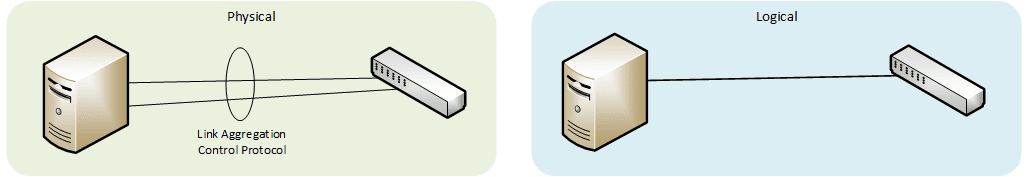
Multi Chassis Link Aggregation Group (MLAG MC-LAG)
Type of LAG where ports terminate on separate chassis in order to improve redundancy in the event one of the chassis fails.
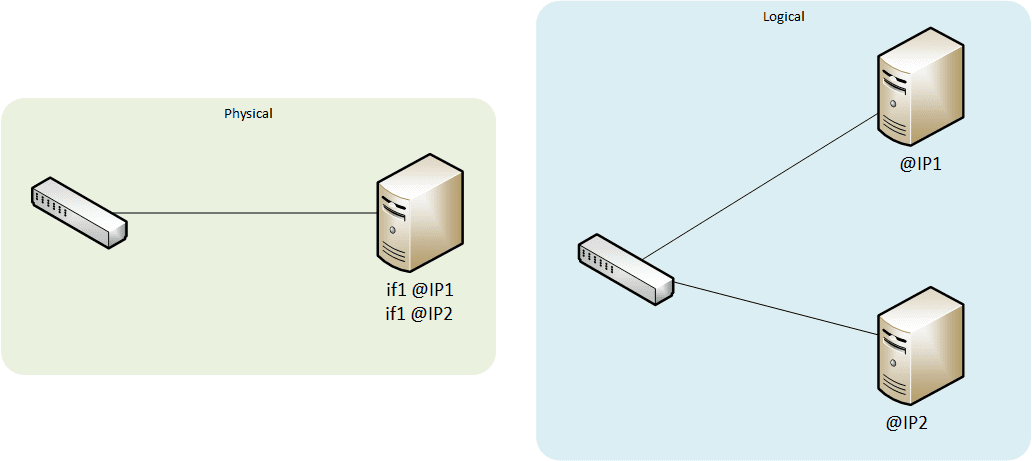
IP aliasing
Use of one single physical interface with several virtual IP adresses.
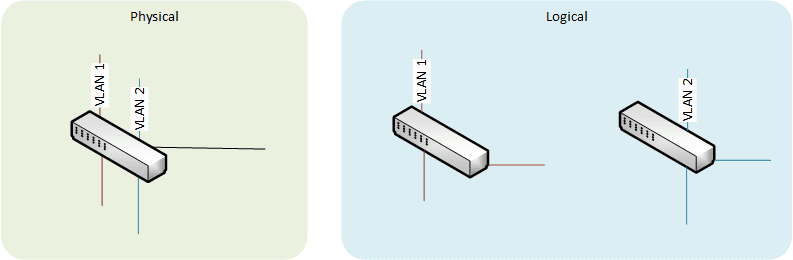
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN)
Creation of several broadcast domains within one single physical switch. Even though it is basically not a security features, it also provides virtual segmentation of a network.
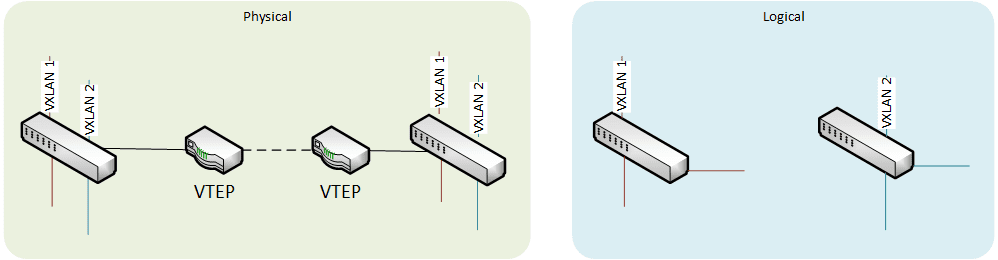
Virtual Extensible Local Area Network (VXLAN)
VLAN like encapsulation of Layer 2 ethernet frames within Layer 4 UDP datagrams. VLANs can now be routed at Layer 3 level between Virtual Tunnel Endpoints (VTEPs).
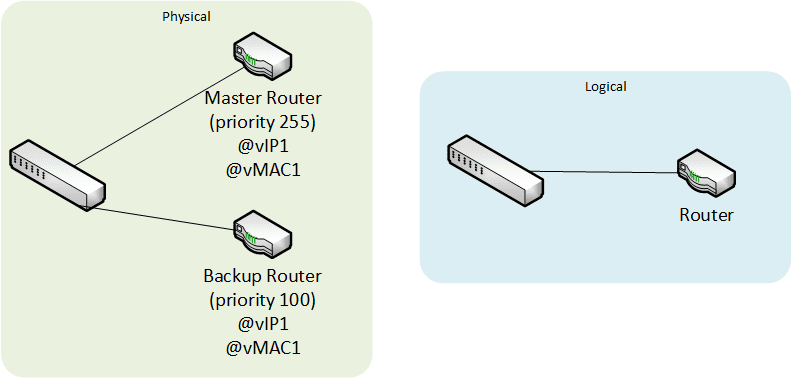
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) / Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP)
Grouping of several routers behind one single MAC adress and IP adress in order to increase the availability of the gateway in case of failure of the master router.
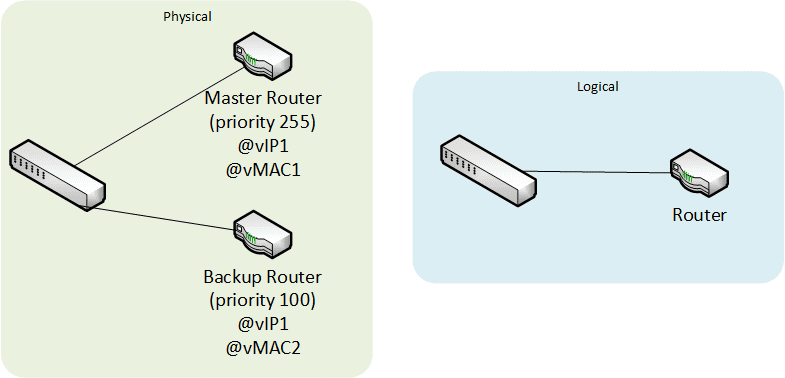
Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP)
Provides the same benefits as VRRP for high availability, but increases the performance thanks to load-balancing features.
Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF)
Creates multiple virtual routers (each with their own separate routing table, independent routing protocols…) from a single physical appliance.
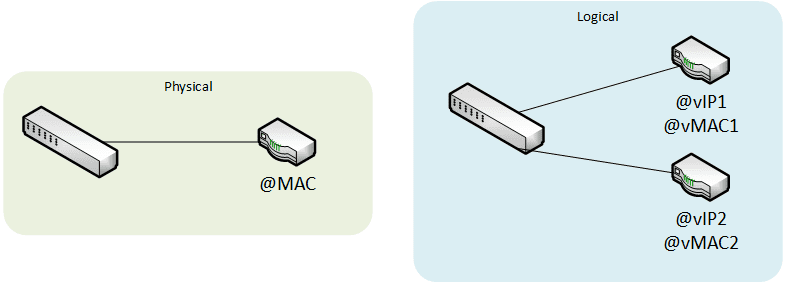
Virtual switching
An hypervisor emulates a switch in order to control the traffic between virtual machines.
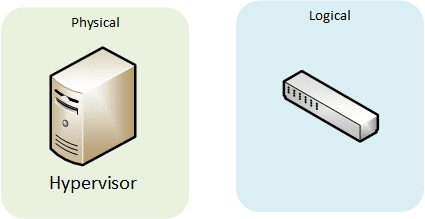
Server virtualization
One single hypervisor hosts several virtual machines (guest operating systems), achieving similar performances to having the applications running on separate hardware instances. It also provides the abstraction of the underlying hardware (CPU, RAM…). It got enhanced with features such as high availability, vMotion, automatic scalabilty, fault tolerance…
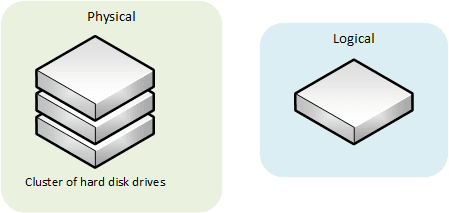
Storage virtualization
With Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID), multiple hard disk drives are aggregated in order to achieve better read / write performance, or higher availability.
Note: Based on original learning material from VMWare documentation VMWare NSX Network Virtualization Fundamentals.